Sustainable Urban Planning in New Blue Area Islamabad: What to Expect
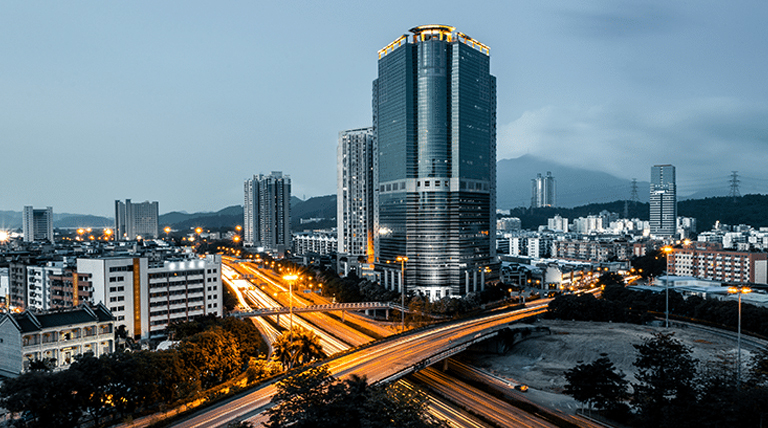

Urban planning in the 21st century has increasingly embraced sustainability as a core principle, ensuring that cities not only accommodate population growth but also safeguard environmental and social well-being. Islamabad, Pakistan’s meticulously planned capital, has become a symbol of thoughtful urban design. As the city grows, new developments like the New Blue Area Islamabad promise to be a showcase of sustainable urban planning in action. This article delves into what to expect from sustainable urban planning in the New Blue Area, highlighting its environmental, social, and economic benefits.
Table of Contents
ToggleA Vision of Modern Urban Sustainability
Sustainable urban planning focuses on creating cities that are resilient, inclusive, and environmentally friendly. For the New Blue Area in Islamabad, this means leveraging advanced technologies, innovative infrastructure, and eco-friendly design to create a model of sustainability. The district is positioned to be a dynamic hub for commerce, business, and social activities while maintaining Islamabad’s serene atmosphere and natural beauty.
1. Energy-Efficient Infrastructure
One of the key expectations from sustainable urban planning in the New Blue Area is the development of energy-efficient infrastructure. With energy consumption being a major challenge in urban areas, the New Blue Area is expected to incorporate smart buildings designed with energy conservation in mind. This includes:
- Green Building Designs: New structures in the area will likely comply with green building standards such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design), ensuring that construction materials, lighting, heating, and cooling systems are environmentally friendly.
- Solar Power Integration: With Islamabad’s ample sunlight, the New Blue Area can tap into renewable energy sources by integrating solar panels on rooftops, street lighting, and other public infrastructure. Solar power not only reduces the dependence on fossil fuels but also provides a long-term, cost-effective energy solution.
2. Sustainable Transportation Solutions
Urban congestion, pollution, and inefficient transport systems are common problems in growing cities. The New Blue Area’s sustainable urban plan will likely prioritize:
- Public Transit Networks: To minimize the reliance on personal vehicles and reduce traffic congestion, the New Blue Area is expected to be integrated into Islamabad’s public transport systems, such as the Metro Bus Service and future expansions like light rail systems. These initiatives will ensure seamless connectivity while reducing carbon emissions.
- Pedestrian-Friendly Design: A shift towards walkable cities is crucial for sustainability. Expect pedestrian zones, wide walkways, and bike lanes that promote non-motorized transportation. These elements foster healthier lifestyles and minimize vehicle emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
- Electric Vehicle (EV) Infrastructure: With the global push towards electric vehicles, the New Blue Area could become a hub for EV adoption. Charging stations and incentives for electric vehicle ownership will be crucial in encouraging residents and businesses to switch to cleaner transport options.
3. Water Conservation and Management
Water scarcity is a growing concern globally, and effective water management is central to sustainable urban planning. In the New Blue Area, innovative approaches are expected to ensure water conservation and efficient usage:
- Rainwater Harvesting Systems: With seasonal monsoons, Islamabad is well-positioned to implement rainwater harvesting in urban developments. The New Blue Area’s buildings and public spaces can collect and store rainwater for various uses, reducing the strain on municipal water supplies.
- Greywater Recycling: Reusing greywater from sinks, showers, and laundries for irrigation and landscaping can significantly cut water consumption. The district’s sustainable urban design should include greywater systems to support its green spaces and public areas.
- Smart Water Management: Smart sensors and meters could be installed in the area to monitor water usage, detect leaks, and manage water distribution efficiently. This proactive approach to water management ensures sustainability and reduces waste.
4. Green Spaces and Urban Biodiversity
Green spaces are a hallmark of Islamabad’s urban identity, and the New Blue Area is expected to continue this tradition by incorporating ample parks, gardens, and tree-lined streets. The benefits of green spaces in urban environments go beyond aesthetics:
- Urban Heat Island Mitigation: The presence of trees and green spaces helps mitigate the urban heat island effect, where concrete and asphalt trap heat, raising city temperatures. By integrating parks and rooftop gardens, the New Blue Area can maintain cooler, more comfortable urban temperatures.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Sustainable urban planning aims to preserve and even enhance urban biodiversity. The New Blue Area could feature native plant species and wildlife habitats that support birds, insects, and other species, fostering a balanced ecosystem within the city.
- Public Health Benefits: Green spaces also contribute to the physical and mental well-being of residents by offering areas for recreation, relaxation, and social interaction. The New Blue Area will likely prioritize community spaces that encourage outdoor activities, enhancing the quality of life for its inhabitants.
5. Waste Management and Recycling Initiatives
Waste management is a major issue in urban areas, and the New Blue Area is expected to adopt modern, sustainable waste solutions to address this challenge:
- Zero-Waste Strategies: The area may implement waste reduction programs, encouraging residents and businesses to minimize waste through composting, recycling, and waste segregation. Zero-waste targets can also be supported by providing convenient recycling centers and incentives for reducing waste generation.
- Smart Waste Management Systems: Advanced technologies, such as smart bins equipped with sensors that monitor fill levels and optimize waste collection routes, can streamline waste management. By reducing the frequency of waste collection trips, fuel consumption, and emissions can be minimized.
- Composting and Organic Waste Processing: Organic waste management will be crucial in reducing landfill contributions. The New Blue Area can integrate composting programs that convert food waste and organic materials into valuable compost for green spaces and landscaping.
6. Mixed-Use Developments and Affordable Housing
A key aspect of sustainable urban planning is the creation of mixed-use developments, where residential, commercial, and recreational spaces coexist. The New Blue Area will likely feature a blend of office buildings, shopping centers, apartments, and cultural spaces, reducing the need for long commutes and fostering a vibrant, self-contained community.
- Affordable Housing: Sustainability is not just about environmental considerations; it also encompasses social equity. The New Blue Area’s urban planning should prioritize affordable housing options to ensure that a diverse range of people, including middle- and low-income families, can benefit from its amenities. This approach not only strengthens community bonds but also prevents socio-economic segregation, a key factor in creating a truly inclusive city.
7. Smart City Technologies
The New Blue Area is expected to integrate smart city technologies to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of urban living. These technologies will include:
- Smart Grids: A smart grid can efficiently distribute energy, balancing supply and demand while reducing energy waste. The grid can also incorporate renewable energy sources, further enhancing the area’s sustainability.
- IoT (Internet of Things): Sensors and connected devices can monitor traffic patterns, air quality, water usage, and other key metrics in real-time. This data can be used to make informed decisions that optimize the performance of urban infrastructure and enhance the quality of life.
- Smart Governance: Digital platforms for public services, such as paying bills, reporting issues, and accessing information, will make governance more transparent and efficient. This reduces bureaucratic inefficiencies and promotes citizen engagement.
The Economic and Social Benefits of Sustainable Urban Planning
Sustainable urban planning in the New Blue Area will deliver economic and social benefits that extend beyond the immediate environmental impact. By embracing sustainability, the district will likely:
- Attract Investment: Businesses are increasingly aligning themselves with sustainability goals. The New Blue Area’s green credentials and cutting-edge infrastructure will attract domestic and international investment, fostering economic growth.
- Create Jobs: Green construction, renewable energy, waste management, and public transport projects will create jobs in the short term. In the long term, the area’s commercial vibrancy will generate employment opportunities in various sectors.
- Promote Social Inclusion: Thoughtful urban design that prioritizes affordable housing, green spaces, and community amenities will ensure that the New Blue Area is an inclusive space where diverse social groups can thrive together.
Conclusion
Sustainable urban planning in the New Blue Area of Islamabad represents a forward-thinking approach to city development, blending economic growth with environmental stewardship and social inclusivity. From energy-efficient buildings and green transportation systems to smart city technologies and biodiversity preservation, the New Blue Area promises to be a shining example of what the future of urban planning should look like. As it evolves, it will not only enhance the quality of life for its residents but also set a benchmark for other cities aiming to embrace sustainability in their growth trajectories.









Post Comment